About Department of Energy and Materials
Opened in April 2022
Study energy, create new technologies
Achieve the SDGs for a brighter future
Energy is innovating like never before. Now is the time to study energy and create new technologies so that the world can reduce fossil fuel use and become carbon free, as well as build a society where people can live in health and comfort.
To contribute to this brighter future and help the world achieve the SDGs, Kindai has established the Department of Energy and Materials.
Graduates who have studied energy and can contribute to the realisation of the SDGs are just what many sectors of industry are looking for. Kindai graduates can work at energy-related companies in the electricity, gas, and petroleum sectors, as well as at manufacturers in industries such as automotive, consumer electronics, housing, medical equipment, materials, textiles, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics.
They can also get teaching licences (for science subjects) or proceed to graduate school.


Find and develop your strengths.
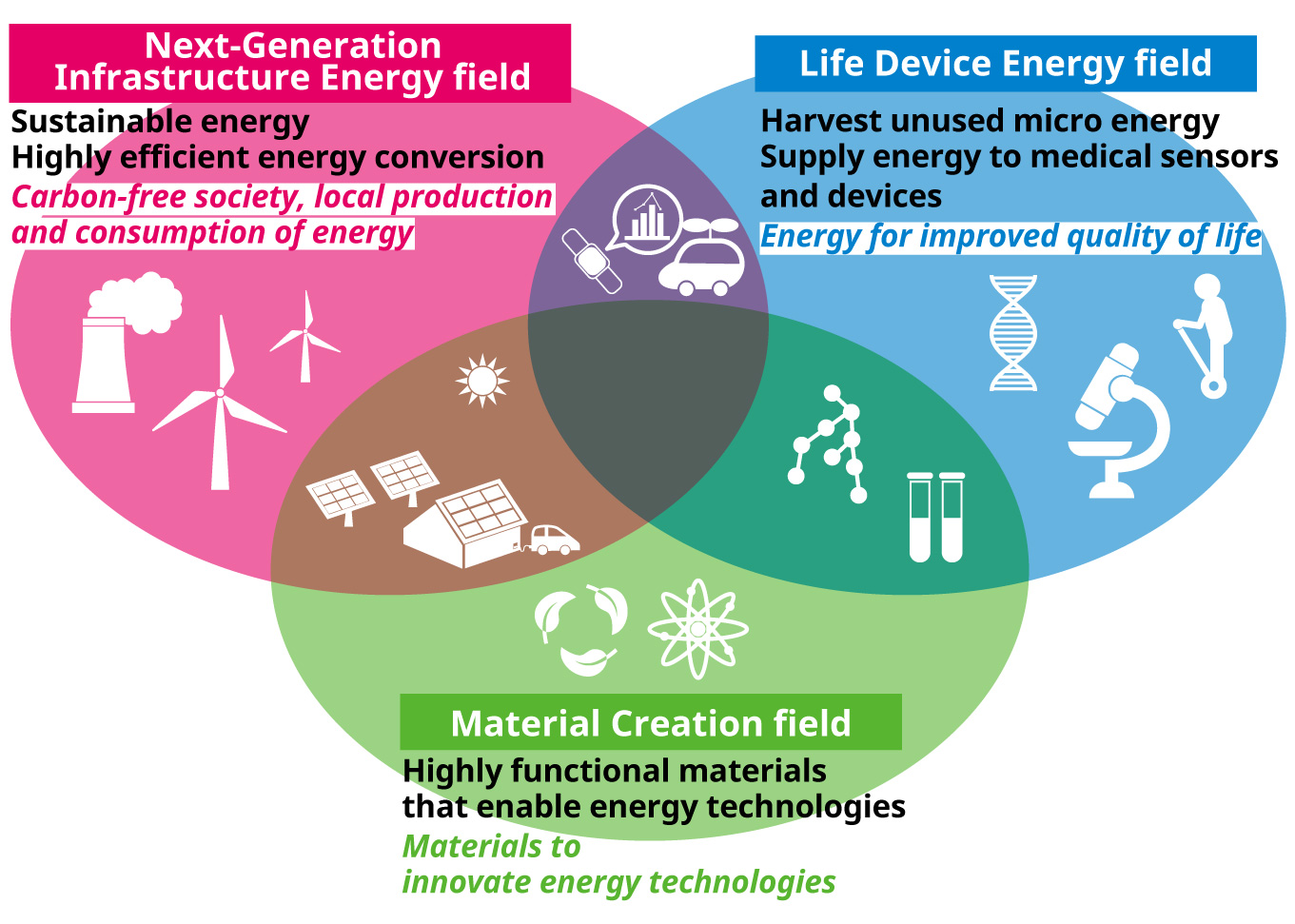
New department comprises three learning fields and three pillars of the energy field.
Education policy: Create a vision for the energy field and foster students who can make this vision a reality.
Society’s needs: Achieve SDGs, build the foundation for Society 5.0.
Foster student’s practical skills to carry out synergistic manufacturing by closely integrating chemistry, electric and electronic engineering, nuclear energy engineering, mechanical engineering, and life sciences.
Message from the Manager of the Department of Energy and Materials

Professor SUDO Atsushi
The instructors in this new department have a range of expertise in areas such as hydrogen, plasma, coordination compounds, macromolecules, solar cells, nuclear physics, mechanics, and life sciences. This department was born of the desire to bring all this expertise together in comprehensive research into energy and materials that would lead to future energy technologies. My wish is to see students learn about the energy conversion at work behind all mechanisms and then use their knowledge towards future manufacturing. I also hope that students will think about the future of energy so that together we can create technologies for a more sustainable future.
Academic Staff

Next-Generation Infrastructure Energy field

- ATSUMI Hisao
- Studying the behaviour of hydrogen in order to develop materials that can store hydrogen.

- ARITOMO Yoshihiro
- Working on the synthesis of new elements, following nihonium.

- OTSUKA Teppei
- Developing materials for safe, airtight storage of hydrogen, radioactive material, and other substances.

- TAKEMURA Yuichiro
- Conducting a range of applied research using plasma.

- NOGAMI Masanobu
- Developing new materials for separating metal ions in aqueous solutions.
Life Device Energy field

- IKEDA Atsutoshi
- Conducting research in measuring human movement and modelling.

- TANAKA Senku
- Conducting applied research in organic materials and organic-inorganic hybrid materials.

- FUCHIHATA Manabu
- Conducting research in carbon neutral energy.

- KONNO Daijiro
- Developing methods for detecting molecular groups that form cells and tissue.

- NAKAZAWA Naotaka
- Conducting research on the role of mechanical strength in brain development and cancer suppression.
Material Creation field

- OKUBO Takashi
- Synthesizing new pigments and applying them to next-generation solar cells.

- KAWASHITA Norihito
- Designing medicines and discovering the mechanisms of diseases.

- SUDO Atsushi
- Making highly strong plastics from plant materials.

- NAKAI Hidetaka
- Making molecules that have the ability to convert energy.

- KITOH Hirotaka
- Using computers to conduct experiments in research on molecules that can be used as materials.
Facilities

- Energy and Materials Lab, 4th Floor, Building 38
Students in the first to third years take the Energy and Materials Experiments class in which they get both theory and practice in physics, chemistry, and life sciences, and in various energy technologies. This gives them the foundations for understanding advanced manufacturing.
Department Overview, Curriculum
Department Overview
| Name | Department of Energy and Materials |
|---|---|
| Start | April 2022 |
| Location | Higashiosaka Campus, Kindai University |
| No. of entrants | 120 |
| Faculty dean | YAMAGUCHI Yoshihiro |
| Department dean | SUDO Atsushi |
| No. of instructors | 15 |
| Degree | Bachelor’s degree (science) |
Curriculum (Excerpt)
| 1st year | 2nd year | 3rd year | 4th year | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lectures and Exercises |
Introduction to Energy and Materials Introduction to Physics for Energy and Materials Introduction to Chemistry for Energy and Materials Experiments in Fundamental Physics Experiments in Fundamental Chemistry 
Experiments in Fundamental Chemistry In all energy-related fields, it is essential to understand the chemical properties of materials and, based on this understanding, have the practical skills to properly handle these materials. In this class, students will get used to basic chemistry experiment procedures by handling familiar subjects, and in the process learn the basics of chemistry. The focus is on metal complexes, chemical batteries, chemiluminescence, and other chemistry topics that form the basis of energy-related technologies. Students also learn the safe handling of chemicals and the proper disposal of experiment waste. Exercises for Mathematics in Chemistry Exercises for Mathematics in Physics |
Introduction to Future Energy Infrastructure
Introduction to Future Energy Infrastructure Students acquire knowledge of next-generation infrastructure energy technologies, which are indispensable to establishing a sustainable society, and the materials behind such technologies. 1–5: Basics of hydropower, thermal power, nuclear power, alternative energy (such as solar, wind, and fuel cells), and power transformation and distribution. 6–10: Materials that make up electronic devices, automobiles, aircraft, and power reactors. 11–15: Energy sources, the electricity situation in Japan, and energy environmental issues. Chemistry of Energy and Materials 1 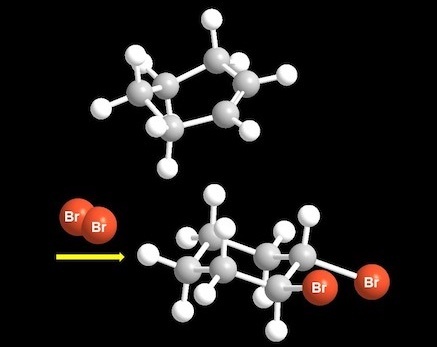
Chemistry of Energy and Materials 1 To understand next-generation energy conversion elements, you need to first understand the structure and electronic states of atoms and molecules, which make up all matter. In this class, students learn why atoms gather to form molecules and why these molecules show different characteristics. Specifically, they study thermodynamic concepts in relation to chemical reactions, stereochemistry and reactivity of simple organic molecules, and various chemical bonds and molecular interactions. Life Device Energy Physics Fundamentals of Biophysics Experiments in Physics for Energy and Materials 1 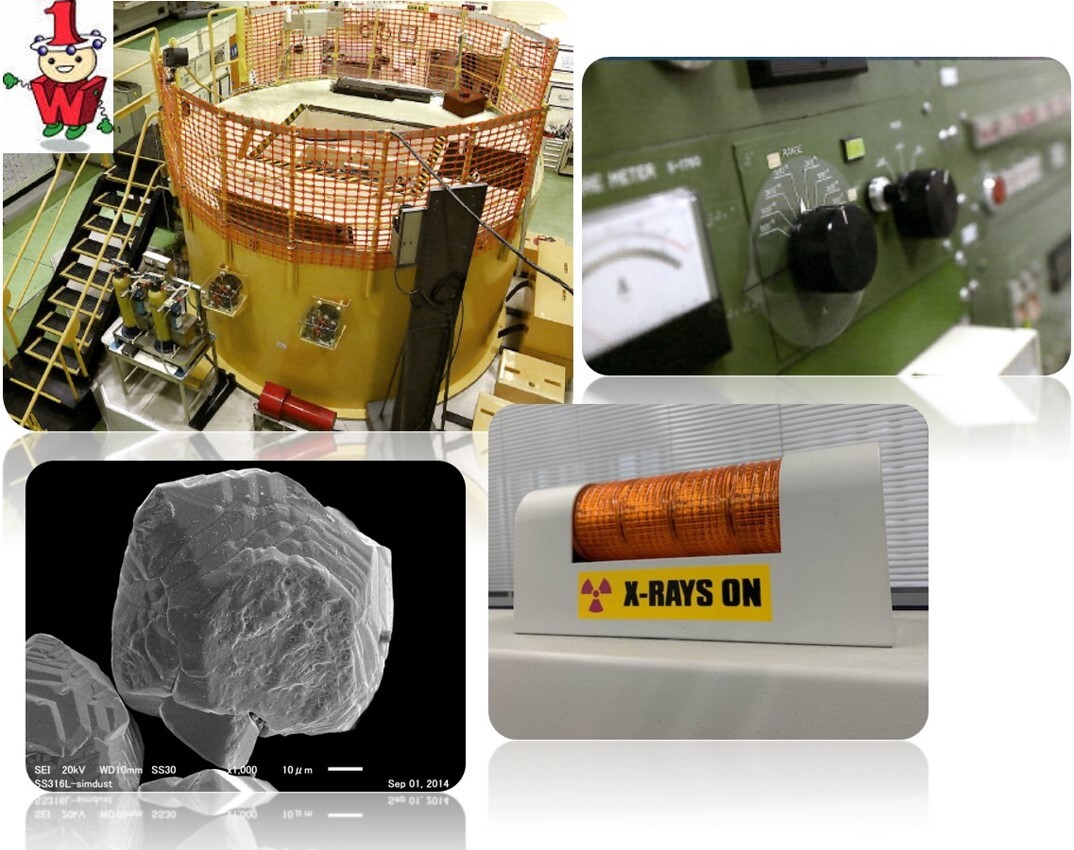
Experiments in Physics for Energy and Materials 1 In this class, students cultivate the basic skills needed to understand energy conversion and control, and to develop various devices, through three main physics experiments: 1. Structure of materials and methods for evaluating physical properties; 2. Photoelectric conversion; and 3. Solid-state physics. In some experiments, they will use Kindai’s research reactor and the facilities of Kindai’s Joint Research Centre to do experiments on electrons, photons, X-rays, and the interactions between ions/neutrons and matter. By creating reports on the experiments, students will learn how to logically present their experiment processes, results, and observations in oral and written form. They will also acquire information literacy, which is needed to analyse data and write reports and explanatory materials. Exercises for Mathematical Analysis Fundamentals of Chemical Information Processing 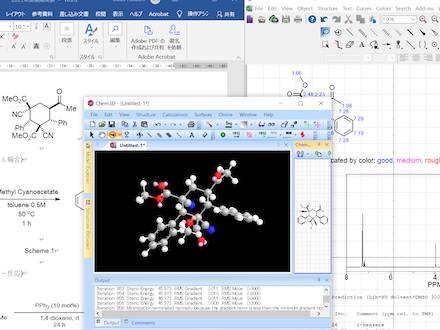
Fundamentals of Chemical Information Processing The effective use of easily understood diagrams and tables is key to writing reports and theses. In this class, students will learn how to effectively use Word, Excel, and other applications in creating presentation materials and reports. As part of their training in AI for chemical substance design, students will also become familiar with the ChemDraw molecule editor and basic Python programming. |
Hydrogen Energy Engineering Electric Energy Generation and Transport Quantum Physics and Engineering 
Quantum Physics and Engineering Radiation is used not only in medicine but also in various other industries. Radiation measurement techniques are indispensable to the proper management and safe use of radiation, which is invisible to the human eye. This lecture gives students basic knowledge of radiation physics and teaches them how to measure and use radiation. The class covers the subjects of physics, practice, and laws and regulations, which are included in the qualification exam for radiation protection supervisor. 1–7: Mechanism behind the generation of radiation, physics concerning the interaction between radiation and matter, principles of measurement. 8–15: Various radiation application technologies, management techniques and laws and regulations pertaining to the safe use of radiation. Molecular Devices Engineering Molecular Functional Chemistry Introduction to Biological Sensors Bioinformatics Engineering 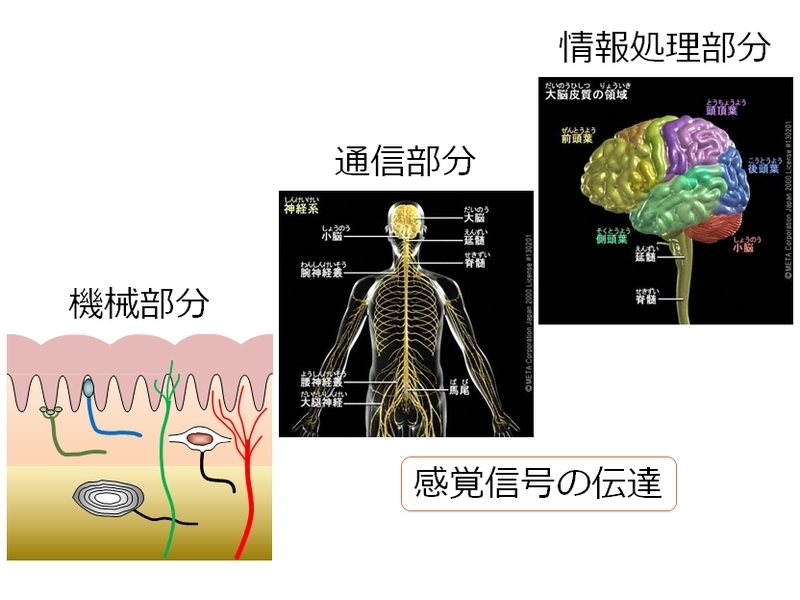
Bioinformatics Engineering This class gives students an understanding of how humans receive and perceive various physical stimuli (such as light, sound, force, smell, and taste) from the real world. They learn about the characteristics of human sensory receptors and the perceptual properties of how the brain processes this information. They also learn about the information processing functions of humans by comparing them with actual sensors. Experiments in Biology for Energy and Materials 
Experiments in Biology for Energy and Materials This course covers 1. cell biology experiments, 2. functions, synthesis, and separation analysis of biological organic materials, and 3. molecular biology experiments on DNA. Through these experiments, students learn to observe and understand life phenomena, understand the correlation between structures and functions of biological materials, and acquire the latest skills in biology experiments. These will form the foundation needed in developing biological devices. 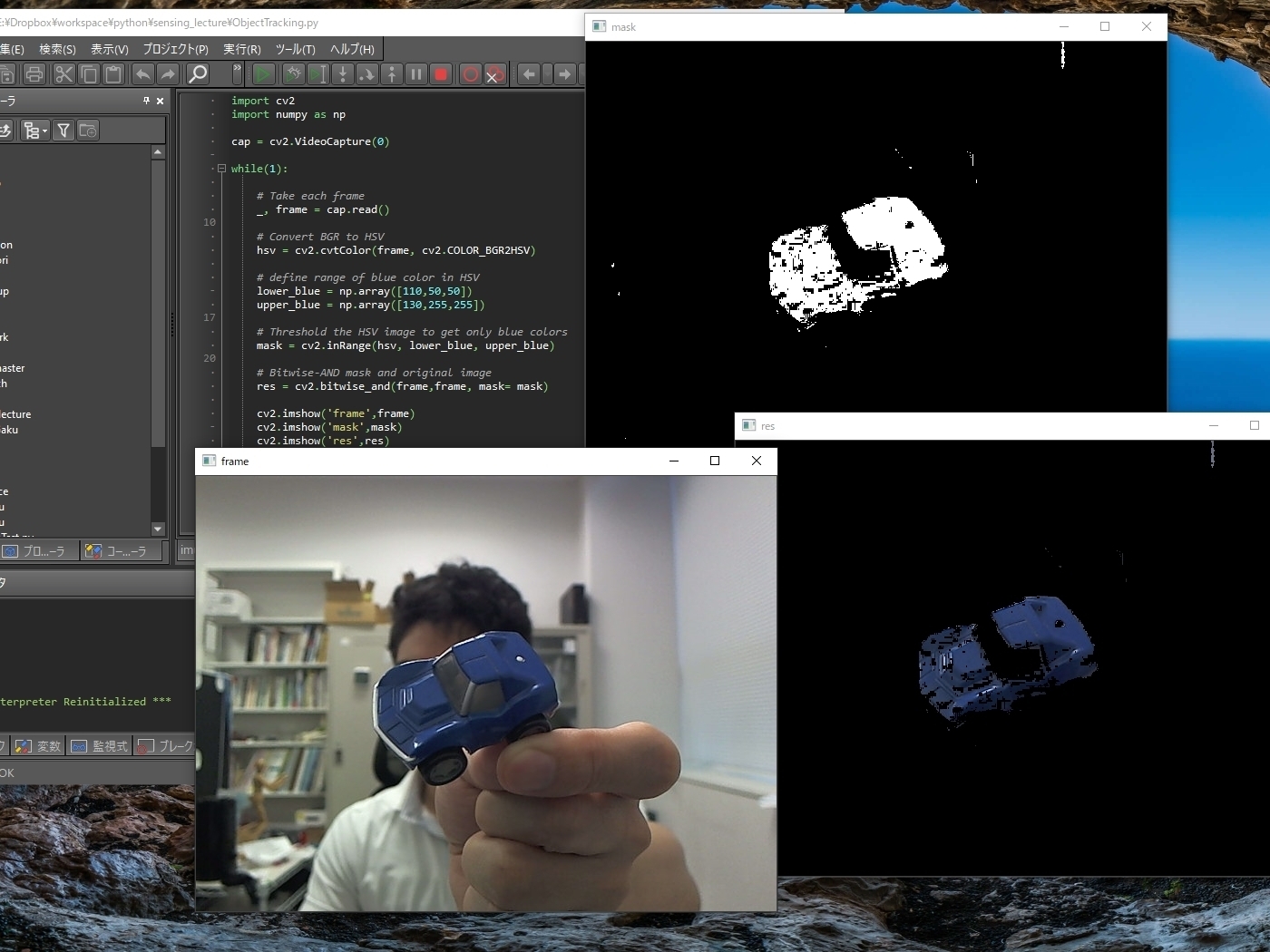
Practice of Informatics Fortran is a programming language used widely today for scientific computation. By using Fortran to write simulation programs, students will shape the mathematical knowledge they have acquired so far into actual programs. Students will also use Python for machine learning and image recognition in order to gain AI knowledge necessary for the future and to practice programming. By acquiring these skills, students gain programming abilities that they can utilise after being assigned to a laboratory. 1–5: Write simulation programs using Fortran. 6–10: Training in machine learning using Python. 11–15: Training in image recognition using Python. |
Individual Study for Bachelor Thesis |
| Small-Group Instruction |
Basic Seminar 1 Basic Seminar 2 |
Seminar on Energy and Materials 1 Seminar on Energy and Materials 2 |
Seminar on Energy and Materials 3 Seminar on Energy and Materials 4 Seminar for Bachelor Thesis |
Qualifications, Certification Tests
Qualifications obtainable with predefined credits
- Type 1 senior high school teaching licence (science)
- Type 1 junior high school teaching licence (science)
- Librarian
All departments in Faculty of Science and Engineering
- IT passport
- Fundamental information technology engineer
Closely related qualifications, certification tests
- Certified energy manager
- Radiation protection supervisor (first class, second class)
- Radiology technologist